
According to the knowledge and technology group,
Excellence in the development of indigenous space technology in the region and increasing the benefit of citizens, businesses and the government from space-based services and technologies as an inseparable part of daily activities is a perspective that is included in the policy document of the country’s space sector in the period from 1401 to 1410. opnions have been asked.
This document describes the major missions of the country as follows:
| Row | Grand missions |
|---|---|
| ۱ | Playing the role of a regional pole and developing space technologies and providing space launch services by relying on the development of local capabilities |
| ۲ | Planning and implementation of space missions in order to benefit citizens, businesses, executive and governance bodies from up-to-date and efficient technologies |
| ۳ | Providing the country’s needs in the field of infrastructure and space services with the aim of reducing service risk, guaranteeing advantages and eliminating bottlenecks |
| ۴ | Developing the necessary platforms to provide the use of up-to-date, efficient and competitive space applications and services at the regional level |
| ۵ | Balanced development of the space industry value chain with the approach of improving commercial indicators and the country’s space sector |
| ۶ | Creation and development of legal, regulatory and structural tools in order to attract and use financial and technical resources in order to improve the space sector of the country with emphasis on benefiting from the capabilities of the knowledge-based private sector. |
| ۷ | Balanced expansion of knowledge, science and space discoveries in the country |
In this document, for the implementation of these policies, 14 major goals are set as follows:
| Row | Big goals |
|---|---|
| ۱ | Localization and stabilization of space technologies required for the design, construction, launch and operation of an optical remote sensing satellite with image resolution better than 5 meters multispectral and 5.2 meters monospectral in class and world standards. |
| ۲ | Localization and stabilization of the space technologies required for the design, construction, launch and operational exploitation of a radar remote sensing satellite with an image resolution of better than 10 meters in a class and world standards. |
| ۳ | Operational presence in the geodetic orbit and localization of technologies required for designing, manufacturing, launching and operating telecommunication satellites in this orbit with the aim of covering the communication needs of the country. |
| ۴ | Localization of key technologies and industrialization of low-orbit satellite systems and space station local navigation assistance system |
| ۵ | Development of sciences, explorations and biospatial based on the design, construction and launch of exploratory payloads and carriers of living organisms for aristocracy and greater mastery over the territory of space and completing the chain of sciences, technologies and space services |
| ۶ | operationalizing the space technologies acquired in the country’s previous space programs as a short-cut solution to meet the country’s space needs to the maximum |
| ۷ | Developing and stabilizing capability, improving reliability and advantage in launching required cargoes to various operational orbits |
| ۸ | Development and completion of infrastructures for technology development, integration, testing, launch and operation of research and operational satellites needed in order to reduce the risks of missions and improve the success rate in carrying out missions through government investment. |
| ۹ | Establishing a national base for space launches to achieve a wide range of orbits, including Khursheed Angag and Earth Angag |
| ۱۰ | Development and networking of multifunctional ground stations for satellite control and spatial data exploitation |
| ۱۱ | Upgrading the platform and creating mechanisms for sharing and processing spatial data for more common access to high-precision satellite images. |
| ۱۲ | Development of space base applications in strategic areas of the country |
| ۱۳ | Development of space-based services in the fields of agriculture, mining, meteorology, crisis management and natural disasters, oil and gas and energy, urban management, environment, Internet of Things, communication of remote and hard-to-reach areas. |
| ۱۴ | Increasing the share of the space-based economy by 5 times from the country’s gross national product and presence in international markets |
The 10-year space document (1401 to 1410) was approved in the last meeting of the Supreme Space Council, and based on it, the country’s goal in the field of space industry is to become one of the countries that export space industry services. This document is specified in one-year, two-year to 10-year horizons in the fields of satellite construction, space infrastructure, space technology development, space base to satellite in different layers. The division of national work is one of the other aspects of this document and it is stipulated to prevent the repetition of projects and research and parallel work.
Excellence in the development of indigenous space technology in the region and increasing the benefit of citizens, businesses and the government from services and basic space technologies as an integral part of the daily activities of the vision of this document has been defined and has set missions for the space industry.
According to this program, the 12th satellite launch of the government in the last two years was “Pars 1” satellite, which was the second satellite of Iran after “Khayyam” and was put into orbit by a foreign launcher. The details of the launched satellites are as follows:
| Row | Satellite | satellite carrier | time warp |
|---|---|---|---|
| ۱ | the Phoenix | Phoenix | The 1400 |
| ۲ | Others 2 | the messenger | March 1400 |
| ۳ | Venus 1 | Winged | June 1401 |
| ۴ | Khayyam | Soyuz | August 1401 |
| ۵ | Suborbital launch | Established 100 | Mehr 1401 |
| ۶ | Suborbital launch of Saman orbital transfer block | – | December 1401 |
| ۷ | The second research launch of Qaim 100 satellite carrier | – | March 1401 |
| ۸ | Noor satellite 2 | the messenger | Mehr 1402 |
| ۹ | Bio capsule launch | Salman launcher | Azar 1402 |
| ۱۰ | Soraya satellite | established | The 1402 |
| ۱۱ | Cradle | Phoenix | February 1402 |
| ۱۲ | Pars 1 | Soyuz | March 1402 |
Two international collaborations for satellite launch
After the launch of Khayyam satellite last year with Soyuz, Pars 1 satellite was the country’s second experience in international launch. “PARS 1” is a survey-research satellite and it has been designed and produced for the purpose of applied imaging, development of domestic measurement data market, and development and testing of technologies required for indigenous operational measurement satellites.
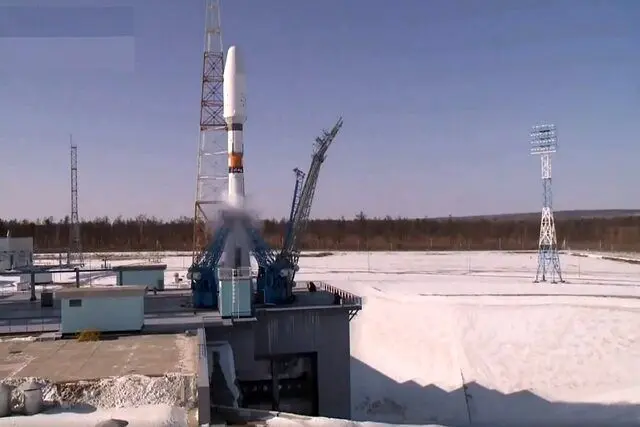

In the infographic below, you can see an overview of the services, equipment and facilities of this satellite:

Dr. Hassan Salarieh in an interview with ISNA. He called the development of indigenous satellite and satellite carrier technologies and increasing the use of space knowledge at the country level as one of the plans of this organization in the space field and said: the use of space capacities in the world is considered one of the emerging fields and the serious plan of the space organization is to take into account the necessity The use and management of spatial data seeks to develop these technologies.
Referring to the country’s space measures in 1402, he said: One of the key measures of the country last year was the start of the design and construction of “PARS 2” and “PARS 3” satellites as newer generations of the “PARS 1” satellite with better and greater accuracy. have been. Pars series satellites are remote sensing and optical satellites capable of imaging the earth’s surface.
Salarieh considered the radar satellite to be one of the serious needs of the country and reminded: the difference between the imaging of radar satellites and optics is that radar satellites are not dependent on the light condition and quality of exposure and can collect the required data from the earth’s surface in cloudy and dusty conditions. .
The head of the Iranian Space Organization stated that there were significant events in the development of data-based services last year, and added: the estimation of the area under cultivation of agricultural products with the help of satellite images in cooperation with the Ministry of Agricultural Jihad has been a significant measure in this field. This cooperation has been needed in the field of preparing spatial maps.
Referring to the projects on the agenda and implemented by this organization, he said: “Pars 2” satellite will be completed in the next few months. Also, the satellite “Talua-3” was unveiled in February 1401; This satellite is a measurement satellite with an accuracy of 10 meters in color and 5 meters in black and white. “Zafar 2” satellite is another project of the organization, which is a sensing satellite with an imaging accuracy of 15 meters.
The head of the Iranian Space Organization emphasized: When these satellites are placed in orbit, they will form a satellite system that can increase the speed of our access to terrestrial data; Because a satellite passes through our area every 12 hours, and when we have several satellites in different orbits, we can shorten the time to access the satellite.
In the field of development of telecommunication satellites, he mentioned the completion of the construction of Nahid 2 satellite as one of the projects on the agenda of the Space Organization and said: Both versions of Nahid 1 and 2 satellites have been completed and the construction of Nahid 3 satellite, which is a telecommunication satellite, has been completed. and has the ability to communicate in higher bandwidth at low altitude, we have finished. Also, a set of microsatellites for the Internet of Things is being built by some private sector companies.
Emphasizing that we have started the feasibility and design of the broadband system, Salarieh continued: Good measures have been taken in the field of launchers, so that some of the country’s launchers are in a stable state. In our country, we started manufacturing liquid, solid and mixed fuel launchers. We had the successful launch of the “Simorgh” satellite carrier in February last year and the launch of the “Qaim 100” satellite carrier in December of last year with liquid fuel. Both satellite receivers are considered important and operational satellite receivers of the country, which have good capacities.
The head of the Iran Space Organization informed about Iran’s step to build heavy satellite launchers and said: We have the design and construction of heavy satellite launchers such as “Serir” and “Qaim 105 and 120” under construction orders.
Development of ground stations
Salarieh continued: One of the infrastructures that is currently being developed in the country is the development of Chabahar ground station. This station provides the country with access to orbits such as Khursheed Anga, the orbit where the Pars 1 satellite is currently located. Also, this station allows providing services to other countries. In line with the development of space infrastructure capacities; We put the development of this station on the agenda and we hope to make the first launch from this area next year.
The head of the Iranian Space Organization noted: With the development of this station, the use of foreign launchers will decrease, but in line with international space cooperation with the target countries, we are also using the capacities of other countries, and in this regard, we are interested in continuing these cooperations.
He described the infrastructure development of Chabahar station as a turning point to reach orbits like Khursheed Anga and said: In the field of space exploration, important events took place, among which we can mention the development of biological capsules and its launch was in the fall of last year. which was a successful launch. This project is considered a starting point for the process of bio-space studies in the country.
Salarieh named the sub-orbital launch of the Saman orbital transfer block as one of the other space achievements of the country and stated: This project is very important for us to access higher orbits, and we implemented the “Saman 1” orbital transfer block and are currently building the block. We are “Saman 2” orbital transition.
He announced the development and completion of laboratories for the assembly and testing of satellites up to 1000 kg in the country and said that the development of the space industry is not possible without round-the-clock efforts and tireless perseverance. Space launches have developed well in the last two years and promise very bright events in the country.
end of message






![بهترین گوشی تا 20 میلیون تومان [فروردین 1403] 11 1711169109 بهترین گوشی تا 20 میلیون تومان فروردین 1403](https://khabarjo.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/1711169109_بهترین-گوشی-تا-20-میلیون-تومان-فروردین-1403-75x75.jpg)









گفتگو در مورد این post